Published on May 24, 2025
How to Use dbd Kali Linux
Kali Linux, the preferred distribution for penetration testers and cybersecurity professionals, comes equipped with a myriad of tools designed to facilitate security assessments and digital forensics. One such tool is dbd (Daniels’ Backdoor), a network backdoor utility that offers remote access capabilities akin to a remote shell, making it invaluable in penetration testing scenarios.
Overview of dbd
dbd is a feature-rich backdoor tool built to facilitate simple, secure, and efficient remote access to compromised systems. It’s designed to be a minimalist tool with a focus on stability and performance.
Key Features of dbd:
- Encrypted Communications: Uses AES-CBC for data encryption, ensuring secure communications between the client and server.
- IPv6 Support: Fully compatible with both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Works on multiple operating systems including Linux , Windows , and macOS .
- Portability: Lightweight and easy to deploy on compromised systems.
Installing dbd in Kali Linux
Kali Linux includes dbd in its repository, making installation straightforward.
Steps to Install dbd
- Update the Repository
sudo apt update
- Install
dbd
sudo apt install dbd
- Verify Installation
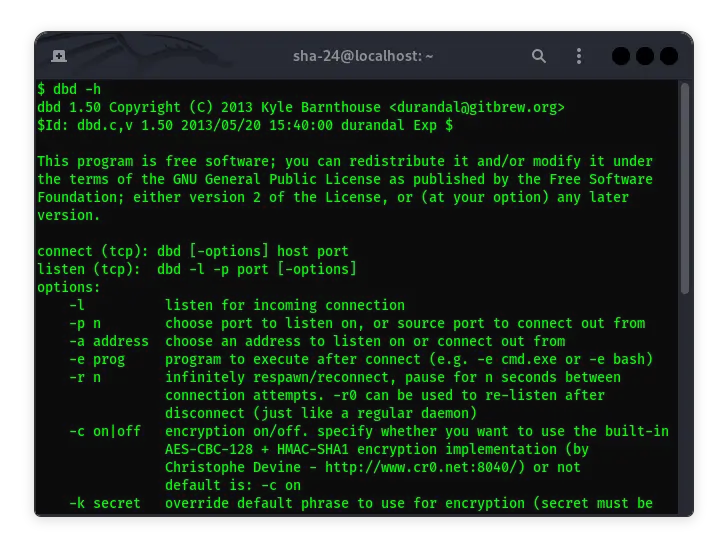
dbd -h
This command should display the help menu of dbd, confirming its successful installation.
Using dbd in Kali Linux
dbd operates in two modes: server mode (listening for incoming connections) and client mode (initiating connections). Here’s how to set up each mode.
Setting Up dbd in Server Mode:
- Command Syntax
dbd -l -p <port_number> -k <encryption_key>
- Example
dbd -l -p 4444 -k secretkey
This command starts dbd in listening mode on port 4444 with “secretkey” as the encryption key.
Setting Up dbd in Client Mode:
- Command Syntax
dbd -c <server_ip> -p <port_number> -k <encryption_key>
- Example
dbd -c 192.168.1.10 -p 4444 -k secretkey
This command connects to a server running on IP 192.168.1.10, port 4444, using “secretkey” for encryption.
Practical Use Case: Penetration Testing
During penetration tests, dbd can be used to establish persistent remote access to a compromised machine. Here’s a typical scenario:
- Compromise a Target System: Use an exploit to gain initial access to the target system.
- Deploy
dbd: Upload thedbdbinary to the target system. - Initiate
dbd: Rundbdin server mode on the target system. - Connect Remotely: Use
dbdin client mode from your Kali Linux machine to connect back to the compromised system.
Security Considerations
While dbd is a powerful tool for penetration testing, it’s essential to use it ethically and within the boundaries of the law. Unauthorized use of backdoor tools like dbd can lead to severe legal consequences.
Best Practices:
- Legal Compliance: Ensure you have explicit permission to test the systems.
- Secure Handling: Always use strong encryption keys and secure the
dbdbinaries to prevent unauthorized access. - Audit and Monitoring: Regularly audit your systems and monitor network traffic to detect and prevent unauthorized backdoor installations.
Detecting and Mitigating dbd
For system administrators, understanding how to detect and mitigate backdoors like dbd is crucial.
Detection Methods:
- Network Traffic Analysis: Use tools like Wireshark to monitor unusual traffic patterns, particularly on uncommon ports.
- File Integrity Monitoring: Employ tools like AIDE to track changes in system binaries and detect unauthorized installations of
dbd. - Log Analysis: Review system logs for unusual activities or connection attempts.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Firewall Rules: Implement strict firewall rules to block unauthorized ports.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploy IDS solutions like Snort to detect and alert on backdoor activities.
- Regular Updates: Keep systems updated with the latest security patches to reduce vulnerabilities that backdoors like
dbdcan exploit.
Conclusion
dbd is a versatile tool in the arsenal of a penetration tester, offering robust remote access capabilities with strong encryption and ease of use. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Proper ethical practices and stringent security measures must be adhered to when using tools like dbd to ensure they are used for legitimate purposes within authorized environments. Understanding both the offensive and defensive aspects of dbd enables security professionals to conduct effective penetration tests while also safeguarding systems against potential misuse.
That’s all the articles from Admin, hopefully useful… Thank you for stopping by…