Published on Apr 11, 2025
OSI Model: Definition, Function, and Explanation of Each Layer
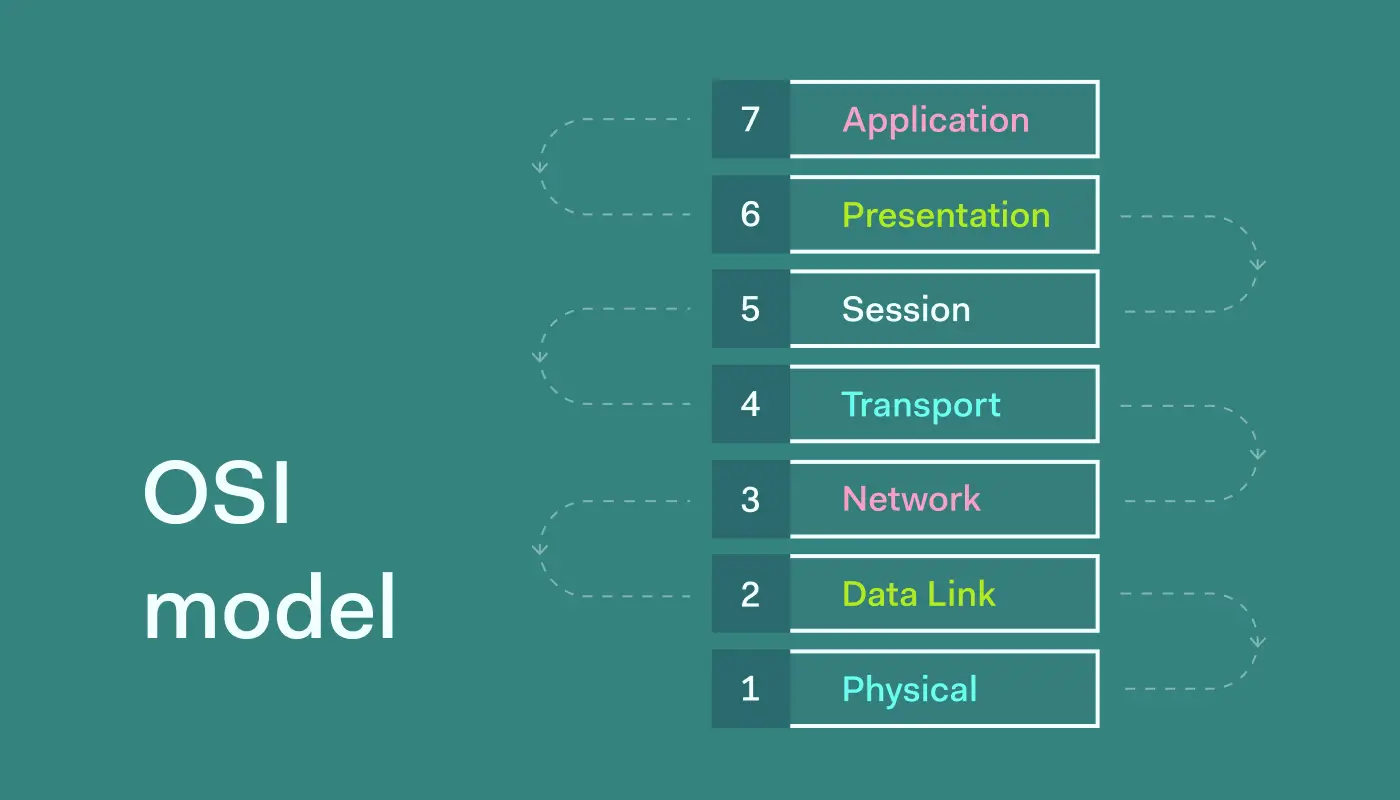
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework used to understand and design how various network protocols interact in a communication system. This model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984. OSI breaks down the computer communication process into seven layers, each of which has a specific function. This model aims to allow better interoperability between various network products and technologies.
Understanding the OSI Model
The OSI model is a reference model that describes how data is communicated over a computer network. It is not a protocol but a guide to designing and understanding how protocols work. This model helps network designers to isolate problems more easily by separating network functions into seven layers.
Functions of the OSI Model
- Protocol Standardization: With the OSI model, the protocols developed can have certain standards that ensure interoperability between different devices.
- Ease of Troubleshooting: Network troubleshooting becomes easier because we can identify problems at a particular layer.
- Separation of Duties: Each layer has a specific task, which makes it easier to develop and modify the network without affecting the entire system.
- Modular Development: By separating functions into layers, development of each part can be done independently.
Explanation of the Seven Layers of the OSI Model
1. Physical Layer
This layer is the lowest in the OSI model and is responsible for the physical transmission of data over a communication medium. The main task of the physical layer is to convert digital data into electrical, optical, or electromagnetic signals that can be transmitted over a physical medium such as copper wire, fiber optics, or radio waves.
Physical Layer Function:
- Determines the specifications of cables, connectors, and physical interfaces.
- Manages the raw bit signals from one device to another.
- Handles the mechanical and electrical aspects of the physical connection.
Example of Devices:
- Hub
- Repeater
- Ethernet Cable
2. Data Link Layer
The Data Link Layer is responsible for data transmission between devices directly connected in a local network. This layer ensures that data is sent correctly by performing physical addressing and error control at the data frame level.
Function of the Data Link Layer:
- Physical addressing (MAC Address).
- Detection and correction of errors in the data sent.
- Controlling access to the network media.
Sub-Layer:
- Media Access Control (MAC)
- Logical Link Control (LLC)
Example of Devices:
- Switch
- Bridge
3. Network Layer
This layer is responsible for logical addressing and routing, which allows data to travel from sender to receiver across various networks.
Network Layer Function:
- Logical addressing (IP Address).
- Routing and forwarding of data packets.
- Controlling network traffic.
Protocols Used:
- IP (Internet Protocol)
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
- IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
4. Transport Layer
The Transport Layer is responsible for end-to-end data delivery between two hosts. This layer ensures that data is sent intact, in the correct order, and without duplication.
Transport Layer Function:
- Data segmentation and reassembly.
- Data flow control.
- Error control.
Protocols Used:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
5. Session Layer
This layer manages communication sessions between applications on two devices. The session layer controls the dialogue between applications, determining when the session starts, ends, and how long the session lasts.
Session Layer Function:
- Manages the dialogue between computers.
- Provides session management.
- Dialogue synchronization.
Protocols Used:
- NetBIOS
- PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
6. Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer is responsible for data formatting. This layer ensures that data sent by the application layer can be read by the application layer on the receiving side.
Presentation Layer Function:
- Data format conversion.
- Data encryption and decryption.
- Data compression.
Supported Formats:
- JPEG
- ASCII
- EBCDIC
- Encryption Formats (SSL/TLS)
7. Application Layer
This layer is the topmost layer and interacts directly with application software to provide various network services to users.
Application Layer Functions:
- Provides an interface for user applications.
- Provides services such as email, file transfer, and web browsing.
Protocols Used:
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
- DNS (Domain Name System)
Conclusion
The OSI model is an essential tool for understanding and developing networking technologies. By breaking down the communication process into seven distinct layers, the model provides a framework that allows different technologies and protocols to work together smoothly. A thorough understanding of the OSI model helps IT professionals in network design, troubleshooting, and developing network applications.
That’s all the articles from Admin, hopefully useful… Thank you for stopping by…