Published on May 24, 2025
Glass Cable: Future Technology for Communication and Data Transmission
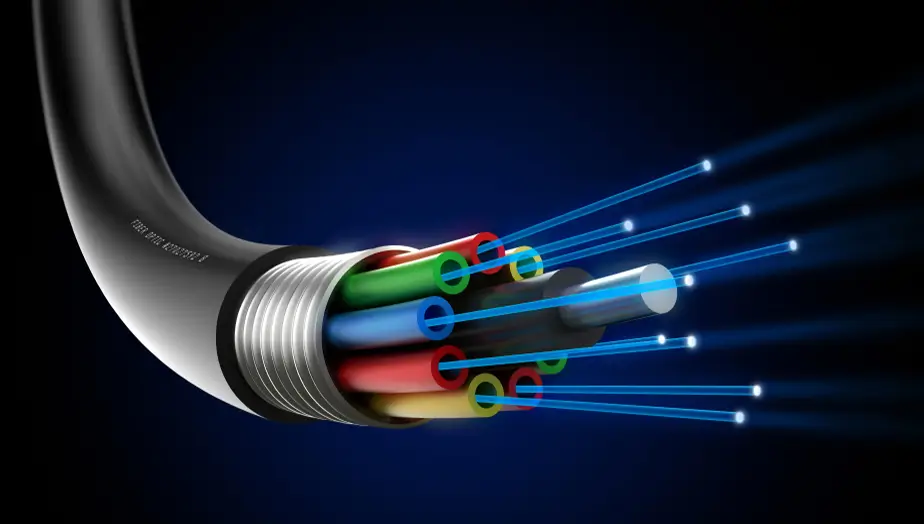
Glass cable, or often called fiber optic, is a type of cable that uses glass or plastic as its basic material to transmit data in the form of light. Compared to conventional cables based on metal such as copper, fiber optic cables are able to transmit large amounts of data at much higher speeds, without being affected by electromagnetic interference. This is what makes it very popular in various sectors, especially telecommunications and the internet.
1. What is Glass Cable (Fiber Optic)?
Glass cable, or fiber optic, is a cable made of very thin and flexible strands of glass. Each strand of glass in this cable is known as an optical fiber and usually has a very small diameter, less than a human hair. This property of glass allows for high-efficiency light transmission so that data can be sent at incredible speeds.
The data transmission process in glass cables uses the principle of total internal reflection, which allows light to move through the fiber without leaving its path. Thus, this fiber optic cable can transmit signals over very long distances without losing much signal.
2. History of Glass Cable Development
The history of glass cable development can be traced back to the 1950s when scientists began looking for alternative solutions to increase the speed and capacity of data transmission. In 1966, Charles Kao and George Hockham, two scientists from England, discovered that glass fibers could be used to transmit data in the form of light if the glass material was pure enough to reduce signal loss.
Kao and Hockham discovered that by using high-quality glass materials, light could transmit data over long distances without losing signals. This finding finally gained widespread recognition, and in 1970, the first commercial fiber optic cable was successfully produced by Corning Glass Works. From here, glass cable technology has developed rapidly until now.
3. How Does Glass Cable Work?
The working principle of glass cable is by using light as a medium for data transmission. Optical fiber consists of three main components:
- Core: The inner part of the optical fiber made of pure glass, where light is reflected and transmitted.
- Clading: A layer around the core that has a lower refractive index, so that it reflects light back to the core.
- Protective layer: Outer layer to protect the fiber from physical damage.
Light is inserted into the core of the optical fiber at a certain angle, so that it bounces along the fiber core. This process is called total internal reflection. Because light reflects without leaving the core, information can be transmitted over long distances without much signal loss.
- Yesterday There Was News About DeepSeek AI Data Leak, What Caused It?
- Easy Guide to Handling Bugs in Software Development
- Safe Strategy for Storing NFTs and Tokens in the Era of AI Hacking
- Complete Guide to Evil-WinRM on Kali Linux
- How to Fix Error "Error writing lock file ./.charge_control_end_threshold.swp: Permission denied"
4. Advantages of Glass Cables compared to Conventional Cables
There are many advantages of glass cables compared to conventional metal-based cables. Some of them include:
- High Speed and Capacity: Glass cables are capable of transmitting data at high speeds and in large quantities, making them very suitable for modern telecommunications needs such as high-speed internet and telephone networks.
- Less Electromagnetic Interference: Unlike metal cables that are susceptible to electromagnetic interference, glass cables are free from interference. This means that data can be transmitted without distortion, making it ideal for environments full of electronic devices.
- Long Transmission Distance: Glass cables can transmit data over longer distances without a signal amplifier compared to metal cables.
- Higher Bandwidth Capacity: Because it uses light for transmission, fiber optics has a very large bandwidth capacity, meaning more data can be transmitted at one time.
- Security: Data transmission using light is harder to intercept than metal cables, making it more secure for sensitive communication needs.
5. Applications of Glass Cables in Various Industries
Glass cables have been used in various industrial sectors. Here are some examples of applications:
- Telecommunications and Internet: The telecommunications industry and internet service providers are the largest users of glass cables. Fiber optic networks enable high-speed internet services needed to support various online applications such as video streaming, teleconferencing, and cloud computing.
- Medical: Fiber optics are used in the medical world, especially in endoscopy, where fiber optics allow doctors to see inside a patient’s body without major surgery.
- Military and Security Industry: Glass cables are also used in military communication systems because of their safe nature and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
- Computer Network Systems: Many large companies use fiber optic cables in their internal network systems to ensure the speed and stability of connections between computers.
6. The Future of Glass Cables
As the need for fast and reliable data transmission continues to grow, the use of glass cables is expected to continue to increase. Several recent technological developments are also underway to increase the efficiency and capacity of optical fibers, including the use of Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology that allows multiple light signals with different wavelengths to pass through a single optical fiber.
In addition, research into the use of optical fibers in quantum technology is ongoing. Quantum technologies, such as quantum computers and quantum communications, could pave the way for revolutionary new applications by harnessing the incredible speed and capacity of optical fibers.
7. Challenges in Using Glass Cables
However, glass cables are not without their challenges. One of the main challenges is the relatively high installation costs compared to metal cables. The process of installing fiber optics requires special equipment and expertise, which can increase costs, especially for networks that span large geographic areas.
In addition, optical fibers are susceptible to physical damage. Although made of flexible glass, optical fibers are still fragile and can break if not handled carefully. Therefore, proper care and protection are essential to maintain the functionality of glass cables.
Conclusion
Glass or fiber optic cables are a revolutionary technology in the world of communications. Their ability to transmit data at high speeds and large capacities makes them an ideal choice for modern networking needs. Despite some challenges in terms of cost and durability, the benefits offered by glass cables far outweigh them, making them a promising future technology in communications and other applications.
As technology advances and data needs continue to grow, glass cables are expected to play an increasingly important role. New technologies such as WDM and quantum communications may further enhance the potential of glass cables in providing reliable, fast, and secure communication solutions.
That’s all the articles from Admin, hopefully useful… Thank you for stopping by…